Представлена версия документа, предназначенная для печати
Вы можете загрузить эту страницу на сайте
| |
Amphibalanus improvisus (Darwin, 1854)
Морской желудь |
Систематическое положение (Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Species):
Animalia >> Arthropoda >> Maxillopoda >> Sessilia >> Balanidae >> Amphibalanus improvisus
 Amphibalanus improvisus
Amphibalanus improvisus
Русское и английское названия. Морской желудь, Baybarnacle, acornbarnacle
Синонимы. Балянус, Balanus amphitrite var. amphitrite (Stubbings, 1967), Balanus Amphitrite vostokensis (Tarasov &Zevina, 1957), Balanus var. denticulata (Stubbings, 1961), Balanus amphitrite var. pallidus (Stubbings, 1961), Вalanus improvisus Darwin, 1854, Balanus ovularis
Нативный ареал. Северная Америка
Современный ареал (мировой и конкретнее в России).
Amphibalanus improvisus относится к видам-космополитам. Он встречается в умеренных и тропических частях Атлантического океана, Северного Ледовитого океана, Балтийского моря, Северного моря, Средиземного моря, Каспийского и Черного моря. Он колонизировал многие районы Мирового океана, включая Индо-Тихоокеанский регион и Австралию, Японское море.
В России этот вид был зарегистрирован впервые в обрастаниях гидротехнических сооружений (ГTC) зал. Петра Великого в 1969 г. (Зевина, Горин, 1971). Звягинцев (2003; 2005) нашел этот вид в обрастаниях всех судов каботажного и портового плавания, обследованных в заливе в период навигации - в конце июля, то есть, в начале периода, когда личинки A. Impovisus начинают осаждаться. В обрастаниях гидротехнических сообружений залива, включая Амурский зал и бухту Золотой Рог, A. improvisus был зарегистрирован почти на всех исследованных объектах как характерный вид сообществ обрастания гидротехнических сооружений. В России встречается в Калининградской области, и от Владивостока до Восточно-Китайского моря.
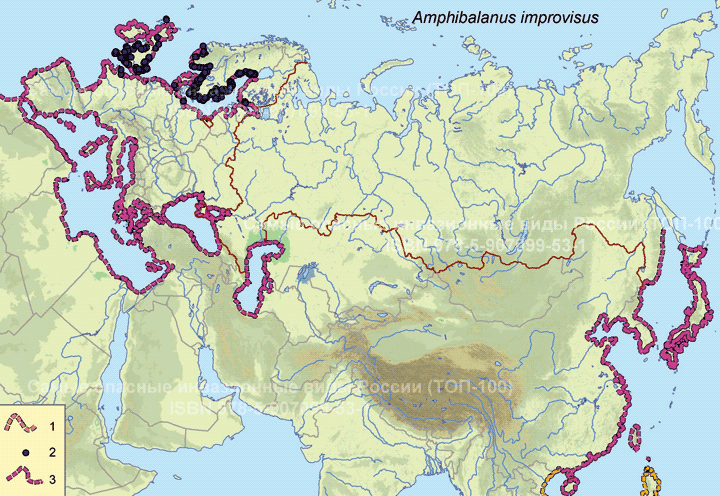
Распространение
Amphibalanus improvisus в Евразии и на Севере Африки
1 – происхождение не ясно, возможно нативен; 2 – места находок; 3 – инвазионная часть ареал.
По: Foffonof et al., 2018 (информационная система NEMESIS, http://invasions.si.edu/nemesis/) с дополнениями.
© Проект РНФ, № 16-14-10323 (Рук. В.Г. Петросян), ИПЭЭ РАН
Пути(коридоры) и векторы (способы) интродукции.
Распространяется как обрастатель на корпусах судов.
Местообитание.
Обитает в эстуариях и солоноваты водах, хотя может переносить и высокую соленость до 40‰ (Foster 1970; Furman & Yule 1991). В устьях рек, он может выживать несколько недель в пресной воде, но для воспроизводства требуется соленость, по крайней мере, 2‰ (Dineen,Hines 1992). Он, как правило, обитает в нижней литорали и сублиторали, в защищенных местах. Он прикрепляется к разным твердым поверхностям: бревнам, камням, корпусам судов, устрицам и другим моллюскам, крабам, морским водорослям.
Особенности биологии.
У балянусов взрослое животное заключено в известковую раковину, которая прикреплена к субстрату и состоит из шести пластинок. Четыре пластинки образуют крышечку и могут раздвигаться благодаря действию специальных мышц. Рачок лежит на дне домика спинной стороной вниз, высовывает конечности между раскрытыми пластинками и совершает ритмичные взмахи, загоняя в домик воду с пищевыми частицами. Относятся к обрастателям, так как прикрепляются своей широкой подошвой к любым подводным предметам — камням, раковинам моллюсков, сваям пирсов и других подводных сооружений, корням деревьев, днищам судов, также могут прикрепляться к различным морским животным. Клейкое вещество, вырабатываемое балянусом для закрепления на поверхности. Балянусы – гермофрадиты, Поэтому возможно как самооплодтворение, так и перекрестное оплодотворение. Развившиеся из яиц личинки свободно плавают и проходят две стадии – стадию науплиуса и стадию циприс. Циприсовидные личинки не питаются, и, попав в подходящие условия, оседают, прикрепляясь к субстрату при помощи передних антенн. Взрослые рачки, после прикрепления ведут неподвижный образ жизни.
Влияние вида (на другие виды, экосистемы включая лесную и агроценозы, здоровье человека).
Балянусы рассматриваются как вредные ракообразные, поскольку могут прирастать тоннами к днищам морских судов, утяжеляя их и снижая судоходную скорость, что приводит к дополнительным затратам по очистке днищ и ежегодным миллионным убыткам стран, владеющих значительным флотом. Существует мнение, что балянусы отчасти виноваты в поражении русской эскадры в Цусимском сражении. Совершив длительный поход из Балтики в Тихий океан, корабли, обросшие колониями морских желудей, заметно потеряли скорость. За год плавания в тропических водах на квадратном метре днища может нарастать до 10 килограммов. Балянусы причиняют также вред как обрастатели, которые портят рыболовецкие снасти, оборудование промышленных предприятий и др. Они опасны для отдыхающих, т.к. имеет твердые раковины, которые могут нанести травму.
С другой стороны, личинки балянусов составляют существенную часть прибрежного морского планктона и в большом количестве поедаются некоторыми планктоноядными рыбами. Рачков употребляют в пищу, поскольку они имеют высокие вкусовые качества и могут использоваться для приготовления супов. В Чили из них делают консервы.
|
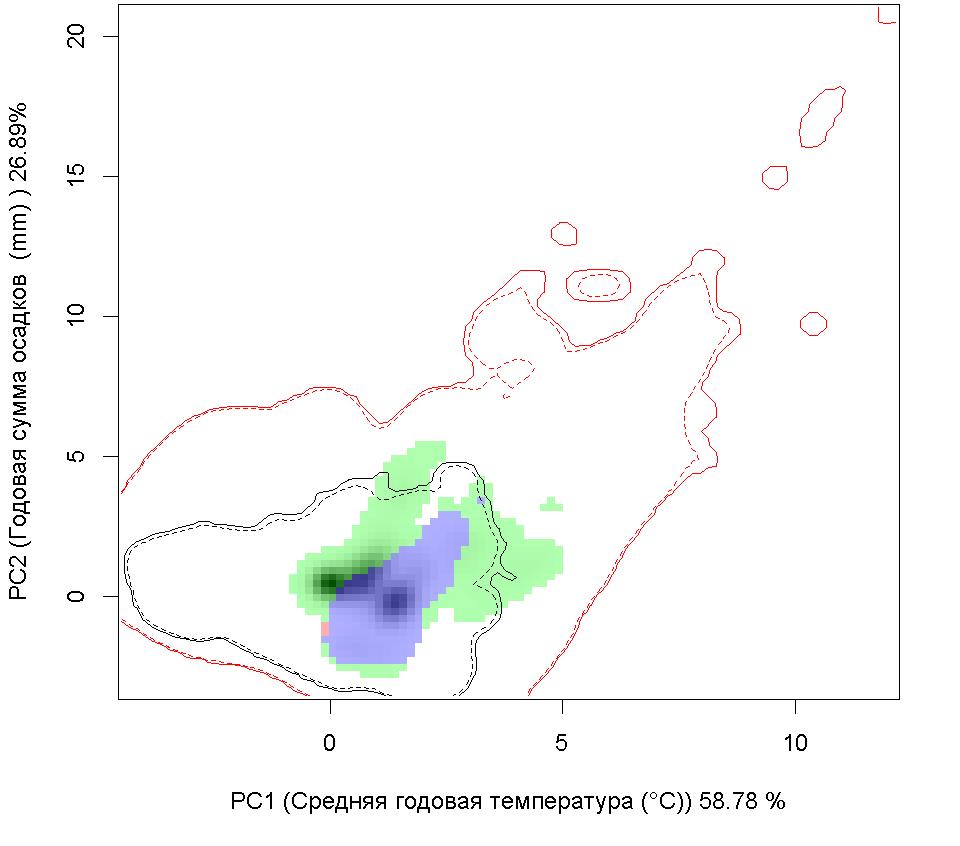
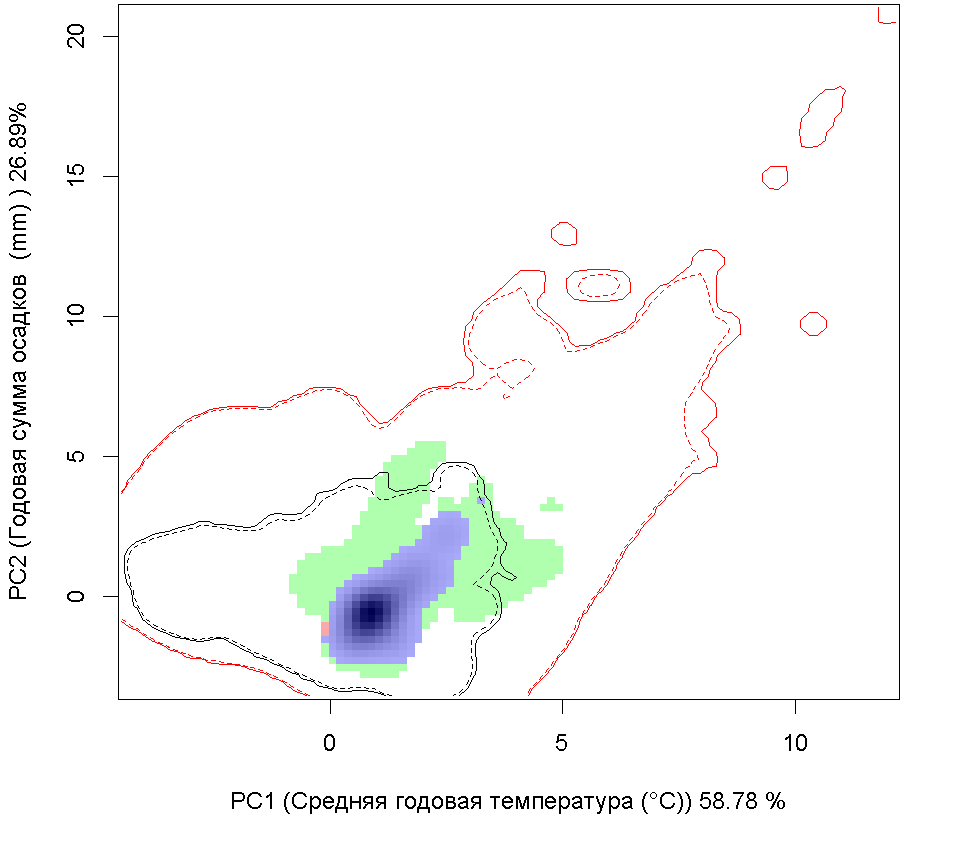
Графическое представление перекрывания ниш нативной и инвазионной частей ареалов, а также при сценариях изменения климата
|
|
Текущий климат
|
|
Нативная часть
|
Инвазионная часть
|
|
 A A
|
 B B
|
| Графическое представление перекрывания ниш нативной (A) и инвазионной (B) частей ареалов вида, где сиреневый цвет – зона стабильности, розовый цвет – зона расширения, зеленый цвет – зона «неиспользования». Сплошные и пунктирные линии показывают 100% и 90% области доступной среды в нативной (черные линии) и инвазионной (красные линии) частях ареалов, которые использовались для анализа перекрывания ниш. |
|
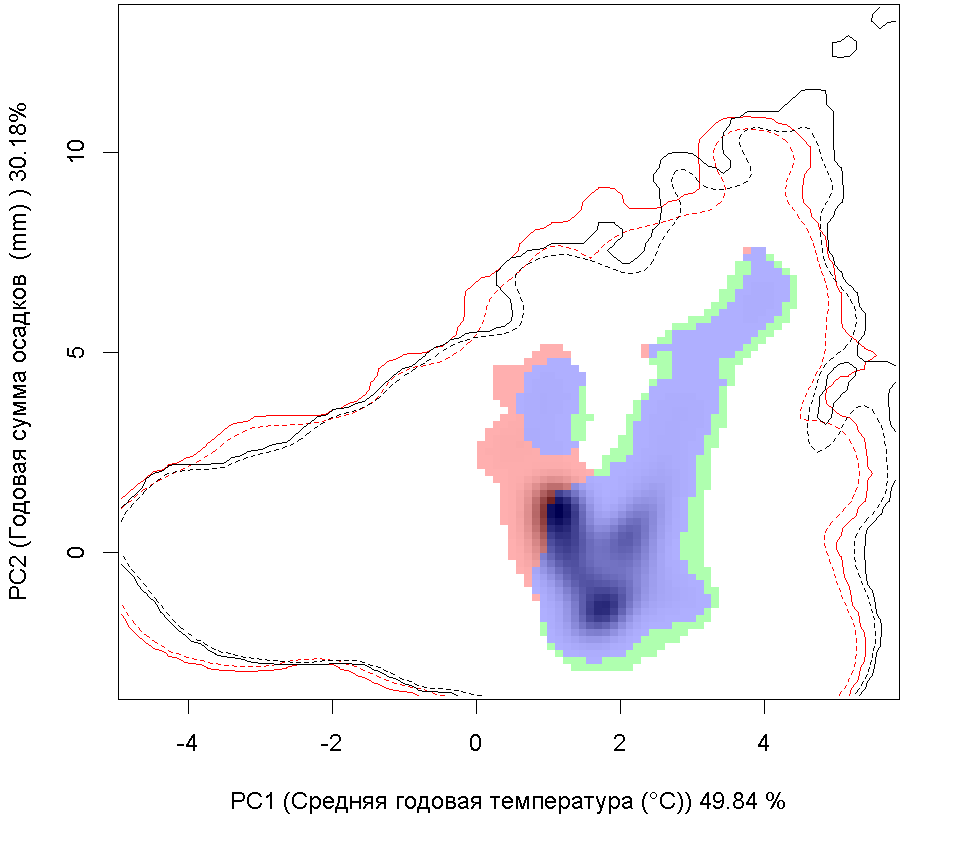
Сценарии изменения климата
|
|
RCP26
|
RCP45
|
|
 C C
|
 D D
|
|
RCP60
|
RCP85
|
|
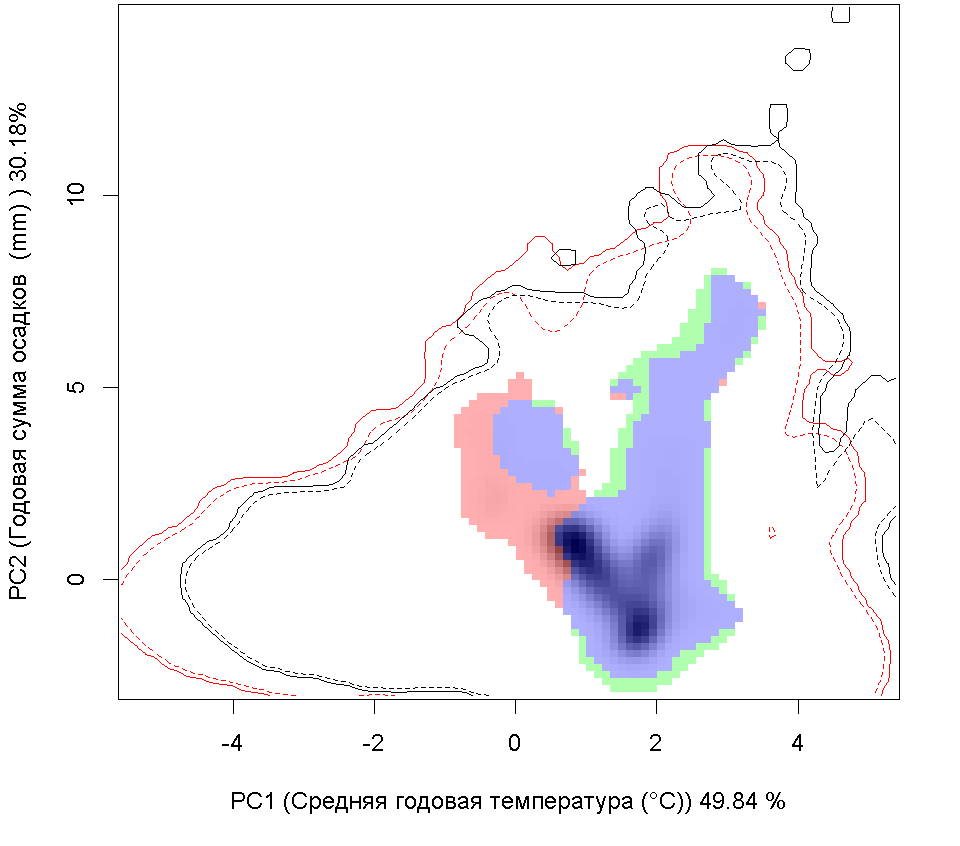 E E
|
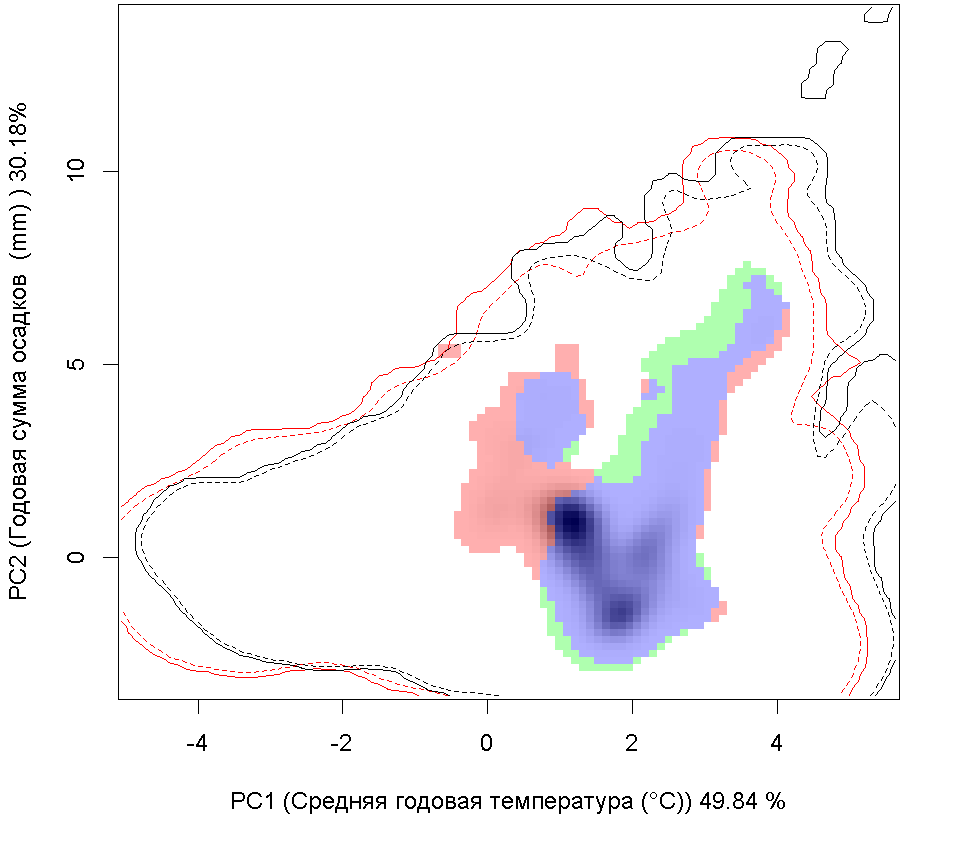 F F
|
| Графическое представление перекрывания ниш в условиях текущего климата и при сценариях его изменения - (C) RCP26; (D) RCP45; (E) RCP60; (F) RCP85. |
Литература
- Farrapeira, Cristiane Maria Rocha (2010) Shallow water Cirripedia of the northeastern coast of Brazil: The impact of life history and invasion on biogeography, Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 392: 210-219
- Foster, B. A. (1970) Responses and acclimation to salinity in the adults of some balanomorph barnacles, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B256: 377-400
- Foster, B. A., Willan, R. C. (1979) Foreign barnacles transported to New Zealand on an oil platform., New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 13: 143-149
- Furlani, Dianne M. (1996) A guide to the introduced marine species in Australian waters., In: (Eds.). . Center for Research on Introduced Marine Pests. Hobart, Australia.
- Furman, E. R.; Yule, A. B. (1991) Balanus improvisus Darwin in British estuaries: gene-flow and recolonisation, Olsen and Olsen, Fredensborg, Denmark. Pp. Pp. 273-276.
- Furman, Eeva (1989) Enzyme genetic variation in Balanus improvisus Darwin (Crustacea, Cirripedia) in the Baltic Sea., Ophelia 30: 35-45.
- Furman, Eeva (1990) Geographical variation of Balanus improvisus in biochemical and morphometric characters., Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 70: 721-740.
- Gislen, Torsten (1950) {On the invasion and distribution of Balanus improvisusalong the coast of Sweden.], Fauna och Flora 45: 32-37
- Godhe, Anna, Wallentinus, Inger (1999) The ports in the Senungsund area, west coast of Sweden, Nordic Council of Ministers, Copenhagen. Pp. 140-183
- Gomiou, Marian-Traian; Alexandrov, Boris; Shadrin, Nikolai; Zaitsev, Yuvenaly(2002) The Black Sea- a recipient, donor, and transit area for alien species., In: Leppakoski, E.; Gollasch, S.; Olenin, S.(Eds.). Invasive aquatic species of Europe: Distribution, impacts, and management.. Kluwer Academic Publishers. Dordrecht. Pp. 341-350.
- Goulletquer, Philippe; Bachelet, Guy; Sauriau, Pierre; Noel, Pierre (2002) Open Atlantic coast of France- a century of introduced species in French waters., Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. Pp. 276-290.
- Graham, Herbert W.; Gay, Helen (1945) Seasonal attachment and growth of sedentary marine organisms at Oakland, California., Ecology 26: 375-386
- Gren, Ing-Marie; Isacs, Lina; Carlsson, Mattias (2009) Costs of alien invasive species in Sweden, Ambio 38: 135-140
- Grigorovich, Igor A.; Therriault, Thomas W.; MacIsaac, Hugh J. (2003) History of aquatic invertebrate invasions in the Caspian Sea., Biological Invasions 5: 103-115
- Henry, Dora P.; McLaughlin, Patsy A. (1975) The barnacles of the Balanus amphitrite complex (Cirripedia, Thoracica)., Zoologische Verhandelingen 141: 1-203
- Holm, Eric R. (2012) Barnacles and biofouling, Integrative and Comparative BiologyPublished online:
- Holopainen, Reetta; Lehtiniemi, Maiju; Meier, H. E. Markus; Albertsson, Jan; Gorokhova, Elena; Kotta, Jonne; Viitasalo, Markku (2016) Impacts of changing climate on the non-indigenous invertebrates in the northern Baltic Sea by end of the twenty-first century, Biological Invasions Published online
- Houghton, D.R. (1971) Barnacles and fouling., In: Gareth Jones, E.B. & Eltringham, S.K.(Eds.). Marine borers, fungi and fouling organisms of wood. Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development. Paris. Pp.
- Iwasaki, Keiji (2006) Human-mediated introduction of marine organisms in Japan: a review., Shoukadoh Book Sellers,and IUCN, Kyoto and Gland, Switzerland. Pp. 104-112.
- Jablonska-Barna, Izabela; Rychter, Agata; Kruk, Marek (2013)Biocontamination of the western Vistula Lagoon (south-eastern Baltic Sea, Poland), Oceanologia 53: 751-763
- Jazdzewski, Kryzysztof; Grabowski, Michal (2011) Alien crustaceans along the southern and western Baltic Sea, Springer, Dordrecht, Netherlands. Pp. 323-344
- Jensen, Kathe R.; Knudsen, Jorgen (2005) A summary of alien marine benthic invertebrates in Danish waters., Oceanological and Hydrobiological Studies 34 (suppl. 1): 137-161
- Jones, Diana S.; Hewitt, Melissa A.; Sampey, Alison (2000) Checklist of the Cirripedia of the South China Sea, Raffles Bulletin of Zoology Supplement 8: 233-307
- Kashin, I. A.; Zvyagintsev, A. Yu;. Maslennikov, S. I. (2000) Fouling of hydrotechnical structures in western Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan., Russian Journal of Marine Biology 26: 89-97.
- Kasymov, A.G. (1982) The role of Azov-Black Sea invaders in the productivity of the Caspian Sea benthos, Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie 67: 533-541
- Kennedy, Victor S.; DiCosimo, Jane (1983) Subtidal distribution of barnacles (Cirripedia: Balanidae) in Chesapeake Bay, MD., Estuaries 6: 95-101.
- Kerckhof, Francis; Haelters, Jan; Gollasch, Stephan G. (2007) Alien species in the marine and brackish ecosystem: the situation in Belgian waters., Aquatic Invasions2: 243-257.
- Kerckhof, Francis; Cattrijsse, Andre (2001) Exotic Cirripedia (Balanomorpha) from buoys off the Belgian Coast., Senckenbergiana Maritima 31: 245-254
- Kim, I-H. (1992) Invasion of foreign barnacles into Korean waters, Korean Journal of Systematic Zoology 8: 163-176
- Kocak, F. ; Kucuksezgin, F. (2000) Sessile fouling organisms and environmental parameters in the marinas of the Turkish Aegean coast., Indian Journal of Marine Science 29: 149-157.
- Korn, O.M. (1999) Distribution of cirripede larvae in Nakhodka Bay, Sea of Japan., Russian Journal of Marine Biology 25: 395-402
- Koryakova, M. D.; Nikitin, V. M.; Zvyagintsev, A. Yu.; Belogurova, L. S. (2002)Effect of polluted harbor waters on fouling and biocorrosion of steel, Russian Journal of Marine Biology 28: 127-131
- Kotta, Jonne and 6 authors (2006) Ecological consequences of biological invasions: three invertebrate case studies in the north-eastern Baltic Sea., Helgoland Journal of Marine Research 60: 106-112.
- Koukouras, Anathasios; Matsa, Athanasia (1998) The thoracican cirriped fauna of the Aegean Sea: New information, checklist of the Mediterranean species, faunal comparisons., Senckenbergiana Maritima 28: 133-142
- Laguna, Jorge (1985) Systematics, ecology and distribution of barnacles (Cirripedia; Thoracica) of Panama., M.S. Thesis, University of California, San Diego. Pp.
- Lang, W. H. (1980) Cirripedia: balanomorph nauplii of the NW Atlantic shores, Fiches D’Identification du Zooplancton 163: 1-6.
- Lang, William H. (1979) Larval development of shallow water barnacles of the Carolinas (Cirripedia: Thoracica) with keys to naupliar stages., NOAA Technical Report NMFS Circular 421: 1-39
- Lang, William H.; Marcy, Martha (1982) Some effects of early starvation on survival and development of barnacle nauplii Balanus improvisus, Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 60: 63-70
- Larsen, Peter F. (1985) The benthic fauna associated with the oyster reefs of the James River estuary, Virginia, U. S. A., Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie 70: 707-814
- Laudien, Jurgen; Wahl, Martin (1999) Indirect effects of epibiosis on host mortality: Seastar predation on differently fouled mussels, Marine Ecology 20: 24-36
- Leppakoski, Erkki; Olenin, Sergei (2000) Non-native species and rates of spread: lessons from the brackish Baltic Sea., Biological Invasions 2: 151-163
- Levings, C. D.; Cordell, J. R.; Ong, S.; Piercey, G. E. (2004) The origin and identity of invertebrate organisms being transported to Canada's Pacific coast by ballast water., Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 61: 1-11
- Llansó, Roberto J.; Sillett, Kristine; Scott, Lisa (2011) Biofouling survey of the Florikan in dry dock, Versar, Inc., Columbia MD. Pp.
- Lozano-Cortés, Diego F.; Londoño-Cruz, Edgardo (2013) Checklist of barnacles (Crustacea; Cirripedia: Thoracica) from the Colombian Pacific, Marine Biodiversity 43: 463-471.
- Lu, L.; Levings, C. D.; Piercey, G. E. (2007) Preliminary investigation on aquatic invasive species of marine and estuarine macroinvertebrates on floating structures in five British Columbia harbours, Canadian Manuscript Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2814: 2-30
- Lutaenko, Konstantin A.; Furota,Toshio; Nakayama, Satoko; Shin, Kyoungsoon; Xu, Jing (2013) Atlas of marine invasive species in the NOWPAP region, Northwest Pacific Action Plan- Data and Information Network Regional Activity Center, Beijing, China. Pp.
- Luther, A. (1950) On the invasion and distribution of Balanus improvisus along the Swedish coast, Fauna och Flora 45: 155-160
- McPherson, Benjamin, Sonntag, Wayne H.; Sabanskas, Maryann (1984) Fouling community of the Loxahatchee River estuary, Florida, 1980-81, Estuaries 7: 149-157.
- Minchin, Dan; Nunn, Julia (2014) The invasive brown alga Undaria pinnatifida(Harvey) Suringar, 1873 (Laminariales: Alariaceae), spreads northwards in Europe, BioInvasions Records 3.
- Montalvo-Urgel, Hugo; Sánchez, Alberto J.; Florido, Rosa; Macossay-Cortez, Alberto A. (2010) [List of crustaceans distributed in submerged woody debris in the tropical wetlands of Pantanos de Centla, southern Gulf of Mexico], Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad 81: S121- S131
- Moore, H. B.; Frue, A. C. (1959) The settlement and growth of Balanus improvisus, B. eburneus, and B. amphitrite in the Miami area., Bulletin of Marine Science of the Gulf and Caribbean 9: 421-440.
- Moore, Hilary B.; Albertson, Helen D.; Miller, Sigmund M. (1974) Long-term changes in the settlement of barnacles in the Miami area., Bulletin of Marine Science24: 86-100
- Naser, Murtada D.;Rainbow, Philip S.; Clark, Paul F.; Yasser, Amaal Gh.; Jones, Diana S. (2015) The barnacle Amphibalanus improvisus (Darwin, 1854), and the mitten crab Eriocheir: one invasive species getting off on another!, BioInvasions Records 4.
- Nasrolahi, Ali; Pansch, Christian; Lenz, Mark; Wahl, Martin (2012) Being young in a changing world: how temperature and salinity changes interactively modify the performance of larval stages of the barnacle Amphibalanus improvisus, Marine Biology159: 331-340
- Nauman, J. W.; Cory, R. L. (1969) Thermal additions and epifaunal organisms at Chalk Point, Maryland., Chesapeake Science 10: 218-226
- Nehring, Stefan (2006) Four arguments why so many alien species settle into estuaries, with special reference to German River Elbe., Helgoland Marine Research60: 127-134
- Newman, William A. (2007) Cirripedia, University of California Press, Berkeley CA. Pp. 475-481
- Noel, Pierre Y. (2011) Checklist of cryptogenic and alien Crustacea of the European Atlantic coast, Springer, Dordrecht, Netherlands. Pp. 345-375
- Nunn, Julia; Minchin, Dan (2013) Marine non-native invasive species in Northern Ireland. http://invasivespeciesireland.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Julia-Nunn.pdf
- Olenin, S., Leppakoski, E. (2000-2016) Inventory of Baltic Sea alien species. http://www.ku.lt/nemo/species.htm
- Orensanz, Jose Maria and 14 other authors (2002) No longer the pristine confines of the world ocean: a survey of exotic marine species in the southwestern Atlantic, Biological Invasions 4: 115-143
- Ortiz, Osvaldo Gomez (1987) Dos neuvos registros de cirripedios (Crustacea) para Cuba., Revista da Investicaciones Marinas 8: 99-100
- Pansch, Christian; Schlegel, Peter; Havenhand, Jonathan (2013) Larval development of the barnacle Amphibalanus improvisus responds variably but robustly to near-future ocean acidification, ICES Journal of Marine Science 70: 805-811
- Partaly, E. M. (1979) Ecology of bryozoan foulings in the Sea of Azov, Soviet Journal of Marine Biology 5: 213-216
- Partaly, Ye. M. (2003) Peculiarities of successions in biocenoses of fouling in the Sea of Azov, Hydrobiological Bulletin 39: 103-112
- Pavlova, E. V.; Murina, V. V.; Kemp, R. B.; Wilson, J. G. ; Parchevsky, V. P.(2007) Annual dynamics of abundance, biomass and survival of meroplankton in Sevastopol Bay, Black Sea, Morskii Ekologicheskii Zhurnal 6: 63-78
- Pearce, John B. (1974) Invertebrates of the Hudson River estuary, Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 250: 137-173
- Pecarevic, M.; Mikus, J.; Cetinic, A. Bratos; Dulcic, J.; Calic, M. (2013)Introduced marine species in Croatian waters (Eastern Adriatic Sea), Mediterranean Marine Science 14: 224-237
- Pilsbry, Henry A. (1916) The sessile barnacles contained in the collections of the U.S. National Museum, including a monograph of the American species., United States National Museum Bulletin 93: 1-366
- Pitombo, F. B. (2004) Phylogenetic analysis of the Balanidae (Cirripedia, Balanomorpha)., Zoologica Scripta 33: 261-276
- Pyefinch, K. A. (1950) Notes on the ecology of ship-fouling organisms., Journal of Animal Ecology 19: 29-35
- Relini, G; Matricardi, G, (1999) Cirripedi toracici delle Lagune Di Orbetello., Atti della Societa Toscana di Scienze Naturali, series B. 86: 55-57
- Riedel, Frank; Audzijonyte, Asta; Mugue, Nikolai (2006) Aliens associating with Caspian Sea endemic bivalves., Biological Invasions 8: 1067-1071.
- Rodríguez-Almaraz, Gabino A.; García-Madrigal, María del Socorro (2014) Ch. 21 [Invasive exotic crustaceans], Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad, . Pp. 337-371.
- Shalaeva, E. A.; Lisitiskaya, E. V. (2004) Seasonal dynamics of the number of larvae of common fouling organisms in Balaklava Bay (Black Sea)., Russian Journal of Marine Biology 30: 371-378
- Skolka, Marius; Preda, Cristina (2010) Alien invasive species at the Romanian Black Sea coast: present and perspectives, Travaux du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle «Grigore Antipa» 53: 443-467.
- Sliwa, Cathryn; Migus, Sasha; McEnnulty, Felicity; Hayes, Keith R. (2009)Chapter 25- Marine bioinvasions in Australia, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg. Pp. 425-437
- Spivey, H. R. (1976) The cirripeds of the Panama Canal, Corrosion and Marine Fouling 1: 43-50
- Sylvester, Francisco and 8 authors (2011) Hull fouling as an invasion vector: can simple models explain a complex problem?, Journal of Applied Ecology 48: 415-423
- Sytsma, Mark D.; Cordell, Jeffrey R.; Chapman, John W.; Draheim, Robyn, C.(2004) Lower Columbia River aquatic nonindigenous species survey 2001-2004: Final technical report, Center for Lakes and Reservoirs, Portland State University, Portland OR. Pp.
- Thompson, Michelle Lynne (1993) Dynamics of an oligohaline, macrofaunal, fouling community., M.S. Thesis, College of William and Mary, Williamsburg VA. Pp.
- U.S. National Museum of Natural History (2002-2016) Invertebrate zoology collections database. http://collections.nmnh.si.edu/search/iz/
- Utinomi, Huzio (1970) Studies on the Cirripedian Fauna of Japan.IX., Distributional Survey of Thoracic Cirripeds in the Southeastern part of the Japan Sea, Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory 17: 339-372
- Vuorinen, Ilppo; Laihonen, Pasi; Lietzén, Erkki (1986) Distribution and abundance of invertebrates causing fouling in power plants on the Finnish coast, Memoranda Societatis pro Fauna et Flora Fennica 62: 123-125
- Ware, Chris et al. (2015) Biological introduction risks from shipping in a warming Arctic, Journal of Applied Ecology Published online.
- Wasson, Kerstin; Zabin, C. J.; Bedinger, L.; Diaz, M. C.; Pearse J. S. (2001)Biological invasions of estuaries without international shipping: the importance of intraregional transport, Biological Conservation 102: 143-153
- Wells, Harry W. (1966) Barnacles of the northeastern Gulf of Mexico., Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences 29: 81-95
- Wittfoth, Anne K. J.; Zettler, Michael L. (2013) The application of a Biopollution Index in German Baltic estuarine and lagoon waters, Management of Biological Invasions 4: in press
- Wolff, W. J. (2005) Non-indigenous marine and estuarine species in the Netherlands., Zoologische Verhandelingen 79: 1-116
- Wonham, Marjorie J.; Carlton, James T. (2005) Trends in marine biological invasions at local and regional scales: the Northeast Pacific Ocean as a model system, Biological Invasions 7: 369-392
- Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, United States Navy Dept. Bureau of Ships (1952) Chapter 10: Species recorded from fouling., United States Naval Institute., Washington, D.C.. Pp. 165-206
- Wrange, Anna-Lisa; André, Carl; Lundh, Torbjörn; Lind, Ulrika; ; Blomberg, Anders; Jonsson, Per J.; Havenhand, Jon N. (2014) Importance of plasticity and local adaptation for coping with changing salinity in coastal areas: a test case with barnacles in the Baltic Sea, BMC Evolutionary Biology 14: published online
- Wrange, Anna-Lisa; Charrier, Gregory; Thonig, Anne; Rosenblad, Magnus Alm; Blomberg, Anders; Havenhand, Jonathan N.; Jonsson, Per R.; André, Carl(2016) The story of a hitchhiker: population genetic patterns in the invasive barnacle Balanus (Amphibalanus) improvisus Darwin 1854, PLOS ONE 11: e0147082.
- Yamanishi, Ryohei; Yokoyama, Hisashi; Ariyama, Hiroyukii (1991)Distributional and seasonal changes of intertidal attaching organisms in relation to water quality along the brackish reaches of the Yodo River., Occasional Papers from the Osaka Museum of Natural History 2: 83-96
- Young, Paulo S. (1994) Superfamily Balanoidea Leach (Cirripedia, Balanomorpha) from the Brazilian coast., Boletim do Museo Nacional (Zoologia) 356: 1-36
- Young, Paulo S. (1998) Maxillopoda. Thecostraca.. Web address: http://acd.ufrj.br/mndi/Carcinologia/hp/Text/Cirripedia.htm
- Zaiko, Anastasija; Lehtiniemi, Maiju; Narscius, Aleksas; Olenin, Sergej (2011)Assessment of bioinvasion impacts on a regional scale: a comparative approach, Biological Invasions 13: 1739-1765
- Zaitsev, Yuvenali; Ozturk, Bayram (2001) Exotic species in the Aegean, Marmara, Black, Azov, and Caspian Seas, Turkish Marine Research Foundation Publication, . Pp. 1-265
- Zevina, G. B.; Goryn, A. N. (1971) Invasion of Balanus improvisus and B. eburneusinto the Sea of Japan., Zoologicheskii Zhurnal 50: 771-773
- Zevina, G. B.; Poltarukha, O. P. (1999) [Barnacles of the Black Sea), Bulletin of the Moscow Society of Naturalists 104: 30-39.
- Zevina, G. B.; Zvyagintsev, A. Yu.; Negashev, C. Z. (1992) [Barnacles of the coast of Vietnam and their role in the environment.], [Institute of Marine Biology], Vladivostok. Pp.
- Zullo, Victor A. (1966) Thoracic cirripedia from the continental shelf of South Carolina USA., Crustaceana 11: 229-244
- Zullo, Victor A. (1979) Marine flora and fauna of the Northeastern United States. Arthropoda: Cirripedia, NOAA Technical Report NMFS Circular 425: 1-29
- Zullo, Victor A., Miller, William, III (1986) Barnacles (Cirripedia: Balanidae) from the lower Pleistocene James City formation, North Carolina coastal plain, with the description of a new species of Balanus da costa, Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 99: 717-730
- Zullo, Victor August (1963) Clasification and phylogeny of the Balanomorpha (Cirripedia), University of California, Berkeley CA. Pp. 1-368
- Zvyaginstev, A. Yu.; Radashevsky, V. I.; Ivin, V. V.; Kashin, I. A.; Gorodkov, A. N. (2011) Nonindigenous species in the far-eastern seas of Russia, Russian Journal of Biological Invasions 2: 164-182
- Zvyagintsev, A. Yu . (1985) Succession of fouling communities of a ship during one navigation in Peter the Great Bay (the Sea of Japan), Soviet Journal of Marine Biology21: 134-140
- Zvyagintsev, A. Yu. (2003) Introduction of species into the Northwestern Sea of Japan and the problem of marine fouling., Russian Journal of Marine Biology 29: 10-21
- Zvyagintsev, A. Yu;. Korn, O. M.; Kulikova, V. A. (2004) Seasonal dynamics of pelagic larvae and settling of the fouling organisms in conditions of thermal pollution., Russian Journal of Marine Biology 30: 266-277
- Zvyagintsev, Yu. A. (1992) Seasonal changes of epifauna on valves of giant oysters in Amur Bay, Sea of Japan, Russian Journal of Marine Biology 17: 71-76
Другие ссылки
http://invasions.si.edu/nemesis/calnemo/SpeciesSummary.jsp?TSN=89622
http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=421139
http://www.europe-aliens.org/pdf/Balanus_improvisus.pdf





